You secure sensitive R&D data at the hardware level by implementing encrypted storage, utilizing Trusted Platform Modules (TPM), and deploying immutable monitoring systems that capture activity directly from physical controllers. Proprietary blueprints and chemical formulas represent constant targets for corporate espionage and physical data extraction. A single breach of your hardware results in catastrophic financial loss and the total erasure of your competitive market advantage. You must move beyond software firewalls and adopt a comprehensive strategy focused on silicon-level defense.

You verify security by conducting deep component audits and establishing hardware-level encryption baselines for all research drives. Integrating aio pc activity recording ensures every verification step remains visually logged for future compliance checks. Professional auditors use specialized oscilloscopes to detect unauthorized power fluctuations indicating data exfiltration through hardware. Establishing a baseline of normal behavior helps your team spot anomalies before they compromise intellectual property.
Conducting regular hardware scans identifies unauthorized chips or modified motherboard headers that bypass your standard security software. You might be wondering how deep these scans actually go.
Monitoring the communication buses prevents malicious actors from tapping into the raw data flow between the CPU and memory. Here is the deal.
Key Takeaway: Verifying security at the hardware level ensures your research foundation remains resistant to sophisticated physical or remote tampering attempts.
| Verification Step | Security Objective | Primary Tool |
| Component Scanning | Detects unauthorized chips | X-Ray/Visual Inspection |
| Encryption Check | Verifies AES-256 status | Firmware Console |
| Bus Monitoring | Prevents data tapping | Hardware Analyzer |
This methodical approach to verification builds a layer of trust that software cannot provide.
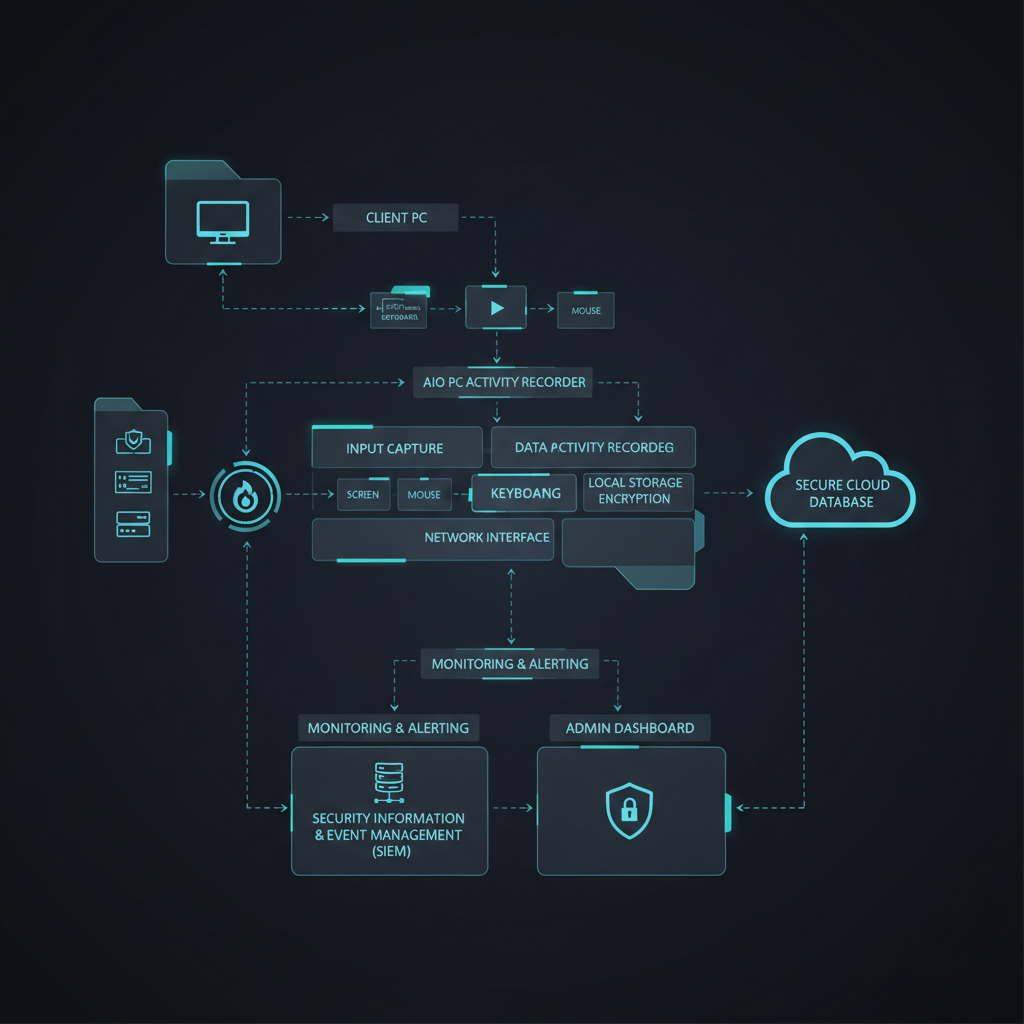
You use hardware-level recording to create unalterable visual logs of every terminal interaction that software-based hackers cannot delete. Standard AIO PC Activity Recording systems capture raw video directly from the display controller to maintain a pure forensic chain. This method provides an immutable visual audit trail that users cannot manipulate or pause during sensitive research sessions. Recording at the hardware level maintains system performance without lagging the heavy R&D applications your team relies on daily.
By capturing data at the hardware controller level, the recording process exists outside the reach of any compromised operating system. What’s the real story?
Visual recordings show exactly what a researcher saw on their screen, including unauthorized attempts to export blueprints or formulas. Wait, there is more.
Key Takeaway: Hardware-based recording provides an unalterable record of all terminal interactions which remains vital for post-incident forensic investigations.
| Controller Capture | Prevents log tampering | Negligible |
| Encrypted Storage | Protects forensic evidence | Moderate |
| Remote Review | Enables off-site auditing | Low |
Visual documentation represents the ultimate deterrent against internal data theft within high-security labs.

Hardware-level security features include Self-Encrypting Drives (SEDs) that keep cryptographic keys isolated within dedicated disk controllers. Using AIO PC Activity Recording alongside SEDs provides a complete picture of who accesses encrypted research volumes while preventing hard drive clicking from compromising data. This setup prevents the main processor from seeing unencrypted data during transmission across the motherboard bus. Modern laboratories demand this level of data-at-rest protection to ensure that physical theft does not result in a data breach.
Secure enclaves provide a physical barrier that prevents malware from scraping encryption keys from the system memory during operation. Think about it.
Offloading encryption tasks to a dedicated drive controller ensures that your high-performance research applications have full access to CPU resources. Ready for the good part?
Key Takeaway: Moving encryption to the hardware controller eliminates software vulnerabilities and significantly boosts performance for high-speed data access.
| Encryption Element | Technical Function | Security Value |
| Dedicated Controller | Offloads CPU processing | High |
| Secure Enclave | Stores cryptographic keys | Extreme |
| Automatic Wiping | Destroys data on tamper | Indispensable |
A dedicated encryption layer ensures your R&D data stays protected even if the entire machine is stolen.

Monitoring the boot process is viable and necessary to prevent low-level rootkits from compromising your R&D workstation before the OS loads. Implementing aio pc activity recording during the initialization phase allows you to detect unauthorized firmware modifications in real-time. Secure Boot technology verifies digital signatures for every piece of hardware before allowing the system to initialize sensitive data. Total visibility during boot stages remains a pivotal defense requirement for any laboratory handling proprietary chemical formulas.
The system checks the digital signatures of every firmware driver against a list of trusted keys stored in the hardware. Believe me.
Recording the boot sequence captures any attempts to load external operating systems or bypass internal security protocols during startup. But here’s the kicker.
Key Takeaway: BIOS-level security establishes a trusted foundation that prevents low-level rootkits from compromising the entire R&D workstation environment.
| BIOS Security Step | Prevention Goal | Implementation Effort |
| Firmware Password | Blocks unauthorized settings | Low |
| Boot Signature Check | Prevents rootkit installation | Moderate |
| Event Logging | Tracks unauthorized boot attempts | High |
Building security from the first millisecond of power-on creates a resilient research environment.

Physical locks prevent leakage by obstructing USB ports and sealing the computer chassis to stop unauthorized data extraction via peripherals. Combining keyed port locks with AIO PC Activity Recording creates a redundant defense against insider threats while identifying clicking drive causes during maintenance. Software-based port blocking can often be bypassed by clever engineers using administrative rights, making physical barriers essential. Visible security measures significantly reduce the temptation for internal data theft among your researchers.
Keyed locks provide a physical barrier that prevents any device from making contact with the electrical pins inside the port. What’s the catch?
Sealing the chassis prevents attackers from accessing internal storage drives or installing hardware keyloggers directly on the motherboard. This is where it gets interesting.
Key Takeaway: Physical locks provide a failsafe barrier that complements digital security by preventing direct hardware access to sensitive data ports.
| Lock Type | Physical Mechanism | Protection Level |
| USB Port Blocker | Plastic or metal insert | Moderate |
| Keyed Port Lock | Requires physical key | High |
| Chassis Security Seal | Visual tamper indicator | Visual Evidence |
Physical hardening ensures that your data remains behind a literal wall of metal and plastic.

Integrating recording systems with the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) ensures that your security software only runs on verified, healthy machines. The TPM chip provides a hardware-based root of trust that anchors your aio pc activity recording logs and protects the drive actuator firmware. The module measures the system state during boot and refuses to release encryption keys if any tampering occurred. Utilizing these chips prevents “man-in-the-middle” attacks where hackers spoof a legitimate laboratory terminal identity.
Every TPM chip contains a unique, non-migratable RSA key that proves the identity of the physical machine to the network. What’s the real story?
Remote attestation allows the security server to verify that the workstation’s hardware and software are in a clean state before granting access. Ready for the good part?
Key Takeaway: Utilizing the Trusted Platform Module creates an unbreakable link between your security software and the physical hardware it protects.
| TPM Function | Security Benefit | R&D Usage |
| Key Generation | Hardware-randomized keys | Continuous |
| Remote Attestation | Proves machine health | Daily Audit |
| Platform Shielding | Prevents password scraping | Permanent |
TPM chips represent the cryptographic heart of a secure research workstation.

A hardware kill switch is necessary when you must guarantee absolute privacy for confidential verbal patent reviews or sensitive visual designs. Even while AIO PC Activity Recording is active, physical switches break the electrical circuit to cameras to prevent remote spying tools. When a researcher flips a physical switch, the peripheral becomes physically incapable of capturing light or sound. This level of privacy proves necessary during highly confidential design reviews where digital mutes are insufficient.
Mechanical switches physically separate the electrical contact points, making it impossible for software to override the “off” state. But here’s the kicker.
Shutter sliders provide a secondary physical layer by blocking the camera lens entirely, even if the electrical circuit is somehow compromised. Think about it.
Key Takeaway: Hardware kill switches provide the only absolute guarantee against unauthorized audio and video surveillance in sensitive research areas.
| Switch Type | Disconnect Method | Reliability |
| Slide Shutter | Physical lens blockage | High (Video) |
| Audio Cut-off | Physical circuit break | Absolute |
| Global Kill Switch | Disconnects all sensors | Maximum |
Privacy is best protected through physical laws rather than complex software code.

Biometrics are required to ensure that the individuals accessing your research terminals are exactly who they claim to be in your security logs. Linking your aio pc activity recording data to a fingerprint scan prevents attackers from using stolen passwords while protecting the hdd cache data. Biometric sensors store templates in secure hardware enclaves rather than in the cloud to prevent wide-scale template theft. Infrared cameras used for identity verification ensure that a living person is actually present at the laboratory desk.
Infrared sensors detect heat signatures and facial depth, preventing attackers from using a simple photograph to bypass facial recognition. You might be wondering.
Linking a biometric scan to every recorded session ensures that there is a clear chain of custody for all research data modifications. Wait, there is more.
Key Takeaway: Biometric authentication ensures that security logs are tied to specific individuals while significantly reducing the risk of credential theft.
| Biometric Method | Accuracy Level | Speed of Access |
| Fingerprint Scan | High | Very Fast |
| Facial Recognition | Moderate/High | Hands-Free |
| Iris Scanning | Extreme | Slow |
Biometrics bridge the gap between human identity and digital data security.

You improve audits by registering unique hardware identifiers and utilizing internal RFID tags to monitor the physical movement of workstations. Real-time AIO PC Activity Recording helps you correlate physical asset movements with the digital interactions occurring on those machines. Digital asset tracking software monitors hardware IDs in real-time across your entire laboratory network to prevent unauthorized swapping. This visibility stops “parts harvesting” where internal employees might steal expensive components for personal use or resale.
Internal RFID tags allow your security team to locate any piece of hardware within the lab building without needing to open the chassis. Believe me.
Monitoring the unique IDs of components like GPUs and CPUs ensures that your high-value hardware has not been replaced with inferior parts. Here is the deal.
Key Takeaway: Continuous asset tracking prevents physical theft and ensures that the hardware configurations in your lab remain exactly as intended.
| Tracking Method | Accuracy | Implementation Cost |
| RFID Tagging | Within 3 meters | Moderate |
| Hardware ID Audit | 100% Digital | Low |
| Asset Database | Administrative | Low |
Keeping a strict inventory of every silicon component prevents slow leaks of your physical assets.

You ensure trust by vetting vendors and inspecting motherboards for unauthorized chips before the workstations are deployed into your R&D lab. Starting with a clean, verified Enterprise SSD and machine is the only way to trust the data captured by your aio pc activity recording system. Professional suppliers provide certificates of authenticity for every component to ensure your equipment comes from a verified source. Knowing the origin of every chip in your machine remains the ultimate level of hardware defense for modern research.
Vetting vendors involves checking their history of security compliance and ensuring they have a secure chain of custody for their parts. What’s the real story?
A detailed BOM lists every single chip and capacitor in your system, allowing your engineers to verify the machine against its original design. Ready for the good part?
Key Takeaway: Establishing a secure supply chain ensures that your hardware arrives without pre-installed vulnerabilities or malicious physical modifications.
| Supply Chain Step | Security Goal | Verification Method |
| Vendor Vetting | Ensures supplier integrity | Background Checks |
| Physical Inspection | Detects motherboard taps | Microscopic Review |
| BOM Verification | Confirms all components | Serial Number Audit |
Securing the supply chain prevents threats from entering your laboratory before you even open the box.
Securing sensitive R&D information requires a shift in perspective from digital-only defense to a holistic hardware-centric approach. We have analyzed how aio pc activity recording provides the visibility needed to deter internal threats and maintain a clean audit trail. Integrating physical port locks, TPM modules, and hardware-level encryption creates a fortress for your most valuable intellectual property. Contact us today to evaluate your current laboratory workstations and identify which physical ports remain exposed. Your future breakthroughs depend on the security measures you establish right now.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can I use software-only solutions to protect my R&D data?Initial findings show software provides a necessary layer but cannot stop physical theft or low-level firmware exploits that occur before the operating system boots.
Q2: What’s the best way to prevent USB data theft in a lab?The most effective method combines physical port blockers with administrative software policies to ensure no unauthorized storage devices ever make contact with motherboard pins.
Q3: Why are physical kill switches better than software mutes?Physical switches are superior because they break the electrical circuit, making it physically impossible for malware to re-enable cameras or microphones without a person present.
Q4: Does recording activity slow down specialized research software?No, hardware-level activity recording uses dedicated controllers to capture the screen buffer, which removes the processing load from the main system CPU.
Q5: How do I know if my hardware has been tampered with?You can detect tampering by inspecting holographic seals on the chassis or monitoring for unexpected hardware ID changes during regular network-based digital audits
